Selection of Methods
1、Two Data Types (Quantitative and Nominal)
The difference between Quantitative and Nominal lies in whether the numerical values have comparative significance.
| Term | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Quantitative | Numerical data with comparative meaning | Satisfaction with Google (Very Dissatisfied, Somewhat Dissatisfied, Neutral, Somewhat Satisfied, Very Satisfied) |
| Nominal | Numerical data representing categories | Gender (Male and Female), Field of Study (STEM and Humanities) |
- Quantitative: Numbers have comparative meaning, e.g., higher numbers represent higher satisfaction or greater height.
- Nominal: Numbers have no comparative meaning, e.g., gender, where 1 represents male and 2 represents female.
2、p value (Sig)
p value (significance value or Sig) describes the probability of an event occurring. A p value less than 0.01 indicates at least 99% confidence in the event, while a value between 0.01 and 0.05 suggests at least 95% confidence.
Researchers study whether purchase intention differs significantly between genders. If the corresponding p value is less than 0.05, it indicates a significant difference at the 0.05 level, implying at least 95% confidence in the result. Most research aims for a p value below 0.05, suggesting influence, relationship, or difference.
Note
Common Standards for p value: 0.01 and 0.05 represent at least 99% or 95% confidence in the occurrence of an event, respectively.
Language Description of p value: Significant at the 0.01 or 0.05 level.
Symbol Representation of p value: Two asterisks (**) for 0.01 and one asterisk (*) for 0.05.
Setting p value Standards: For additional thresholds, such as p < 0.001, click on the user profile in the upper-right corner to customize settings.
3、Select Analysis Methods
Once the two data types (Quantitative and Nominal) are understood, identify X and Y variables. For instance, if X is gender (Nominal) and Y is height (Quantitative), the relationship between X and Y should be analyzed using ANOVA.
SPSSAU Recommendation: Summarize your research question in one sentence. Break it down into X and Y, then match their data types to the appropriate analysis method. Refer to the table below for common methods:
| Analysis Method | Function | Example Sentence | Data Types |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Percentage | What is the gender ratio? | Nominal |
| Descriptive Statistic | Mean | What is the average height? | Quantitative |
| Cross Tabulation (Pearson Chi-square) | Difference | Do different genders (X) smoke (Y) differently? | X (Nominal) |
| Y (Nominal) | |||
| Categorical Summary | Difference | What is the sales distribution by city? | X (Nominal, optional) |
| Y (Quantitative/Nominal) | |||
| One-way ANOVA | Difference | Are there differences in height (Y) among income groups (X)? | X (Nominal) |
| Y (Quantitative) | |||
| Two-way ANOVA | Difference | How do gender (X) and region (X) affect height (Y)? | Y (Quantitative) |
| X (Nominal, two items) | |||
| Three-way ANOVA | Difference | How do gender (X), region (X), and nationality (X) affect height (Y)? | Y (Quantitative) |
| X (Nominal, three items) | |||
| Independent-samples t Test | Difference | Are there differences in height (Y) between genders (X) with only two categories (e.g., male and female)? | X (Nominal) |
| Y (Quantitative) | |||
| One-sample t Test | Difference | Is height significantly different from 1.8? | Quantitative |
| Paired t Test | Difference | Compare students' scores before and after the experiment to assess the difference in their performance. | Pair 1 (Quantitative) |
| Pair 2 (Quantitative) | |||
| Post-hoc Multiple Comparison | Difference | What are the detailed differences in height (Y) among income groups (X)? (e.g., pairwise comparisons) | X (Nominal) |
| Y (Quantitative) | |||
| Normality Test | Normality | Is the data normal? | Quantitative |
| Non-parametric Test | Difference | When height data is non-normal, analyze the difference relationship between income (X) and height (Y). | Y (Quantitative) |
| X (Nominal) | |||
| Correlation | Correlation | Is there a relationship between height (X) and weight (Y)? | X (Quantitative, optional) |
| Y (Quantitative, optional) | |||
| Linear Regression | Impact | Does height (X) affect weight (Y)? | Y (Quantitative) |
| X (Quantitative/Nominal) | |||
| Stepwise Linear Regression | Impact | Automatically identify factors (X) influencing height (Y). | Y (Quantitative) |
| X (Quantitative/Nominal) | |||
| Hierarchical Linear Regression | Impact | Analyze the impact of height (X, Stratum 1) on weight (Y) while considering diet habits (X, Stratum 2). | Y (Quantitative) |
| Stratum 1 (Quantitative/Nominal) | |||
| Stratum 2 (Quantitative/Nominal) | |||
| Stratum 3 (Quantitative/Nominal) | |||
| Stratum 4 (Quantitative/Nominal) | |||
| Binary Logistic Regression | Impact | What factors (X) influence whether people buy movie tickets (Y)? | Y (Nominal,2 values) |
| X (Quantitative/Nominal) | |||
| Multinomial Logistic Regression | Impact | What factors (X) influence the type of movie tickets (Y) people buy? | Y (Nominal,2+ values) |
| X (Quantitative/Nominal) | |||
| Cluster | Group Classification | Divide 300 people into groups. | Quantitative |
| Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) | Summarization | Summarize 30 sentences into 5 key factors. | Quantitative |
| Weight | Determine the weight of each factor representing the 30 sentences. | ||
| Principal Component Analysis (PCA) | Summarization | Summarize 30 sentences into 5 key components. | Quantitative |
| Weight | Determine the weight of each principal component representing the 30 sentences. | ||
| Scatter Plot | Data Relationship | Analyze the relationship between height (X) and weight (Y), distinguished by gender (Color). | Y (Quantitative) |
| X (Quantitative) | |||
| Color (Nominal) | |||
| Histogram | Normality | Does the height data follow a normal distribution? | X (Quantitative) |
| Box Plot | Data Distribution | Display the distribution of height data. | X (Quantitative) |
| Word Cloud | Data Visualization | Show the most common words customers use in feedback about a product. | X (Quantitative) |
| Weight (optional) | |||
| Reliability | Reliability | Is the questionnaire data reliable? | Quantitative |
| Validity | Validity | Is the questionnaire data valid? | Quantitative |
| Item Analysis (Discrimination Analysis) | Discrimination | Do the scale items in the questionnaire have sufficient discrimination? | Quantitative (Scale) |
| Entropy Method | Weight | What is the weight distribution of the data? | Quantitative |
| Multiple Choice | Percentage | How to analyze multiple-choice questions in questionnaire data? | Multiple Choice |
Note:
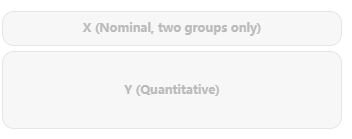
In SPSSAU, the right-side analysis panel shows the required data types for each method. For example, for an independent samples t test examining gender differences in satisfaction, the panel will display as follows:
SPSSAU offers 13 modules (including general methods, data processing, visualization, medical research, econometrics, machine learning, text analysis, advanced methods, meta-analysis, power analysis, etc.), with a total of 500 methods and tests. Simply search for the method's abbreviation or keyword in the top-left search bar to access it instantly.